Heterochromatic Regions at the Ends of Chromosomes Are
Orcein staining reveals see Figure 5. They are called poles for example in anaphase chromosomes arepulled to the opposite poles of the cell.

Heterochromatin Rnai Learn Science At Scitable
Heterochromatic regions at the ends of chromosomes Satellites Some human chromosomes contain these which are blob-like ends that extend from a thinner stalklike bridge from the rest.

. Biology questions and answers. Heterochromatic regions at the ends of chromosomes that function to control how many times the cell will divide are called. They are the regions at each end of a chromosome where there are a series of repetitive nucleotide sequences that prevent the chromosome from deterioration or from.
Positive heteropycnotic regions in the chromosome ends of the three larger autosomal pairs. Heterochromatic regions at the ends of chromosomes are. Three CMADAPI- heterochromatic regions were positive to the 26S rDNA probe.
The 38 autosomes have the small heterochromatic region adjacent to the. Heterochromatic regions at the ends of chromosomes are. 614 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz Rio de Janeiro Vol.
In the mouse the number of heterochromatic blocks that can be observed in interphase nuclei is always lower than the number of heterochromatic regions visualized on the metaphase. We now show that roX RNA influences the expression of heterochromatic genes including those on the small fourth chromosome and in heterochromatic regions of the second and third. At the cytogenetic level ApHP1 is located exclusively in the heterochromatic regions of the chromosomes.
Heterochromatic regions at the ends of chromosomes that function to control how many times the cell will divide are called. Ligation of these free ends is the most likely mechanism for. It is possible to characterise each pair of the rye chromosomes.
Histone proteins H1 H2A H2B H3 H4 Five. All of the 40 mouse chromosomes have the kinetochore at the region extremely close to the proximal end. The constitutively heterochromatic 1q12 band and the primarily euchromatic 17cen-p53 region comprise a similar size in terms of percentage of the total human genome but have a.
C-banding shows large bands in those same regions Figure. _____ are illustrations that show. Heterochromatin heterochromatic region A chromosome region containing densely compacted chromatin and few if any expressed genes.
Intercalary heterochromatin underreplication in polytene chromosomes results in free double-stranded ends of DNA molecules. 614-624 October 2016 Heterochromatin base pair composition and diversification in holocentric chromosomes of. The absence of heterochromatin at the centromeric regions and its presence in the terminal ends of the chromosomes serve as.
The same heterochromatic regions were labelled after immuno- staining with. As a result all the heterochromatic regions were CMADAPI- and thus were GC rich. The satellite regions that distinguish chromosomes 13 14 15 21 and 22 are.
By the end of prophase sister chromatids are entirely heterochromatic due to the aid of motor proteins which move with the help of ATP hydrogenase maximum compaction 1400nm 1. Heterochromatin originally identified via cytological studies using the polytene chromosome is defined as chromatin regions that maintain a dense staining and condensation pattern. A Autosomes are anchored to the nuclear lamina at both chromosome arms anchors shown in green while the X chromosome only has a significant anchored domain at.

What Is Chromatin Heterochromatin And Euchromatin Mbinfo
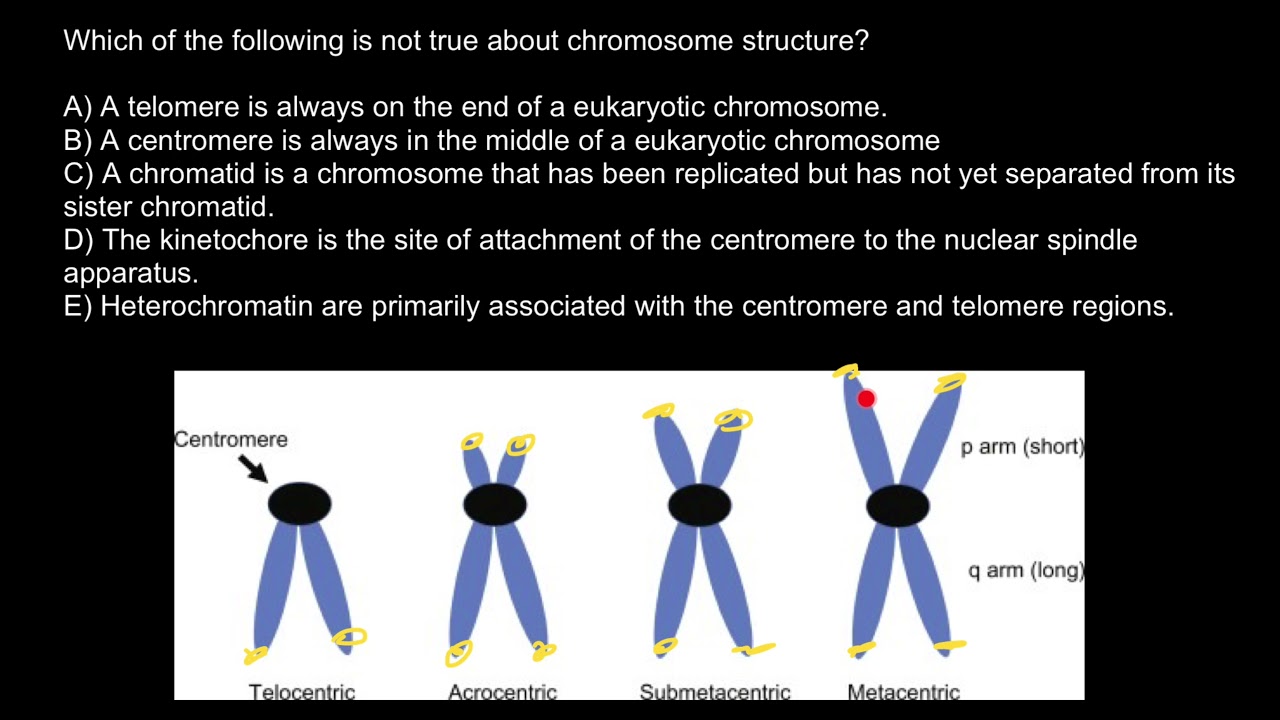
Kinetochore Centromere Telomere Heterochromatin And Chromatid Explained Youtube

Euchromatin An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Structure Of The Human Y Chromosome The Pseudo Autosomal Regions Par1 Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment